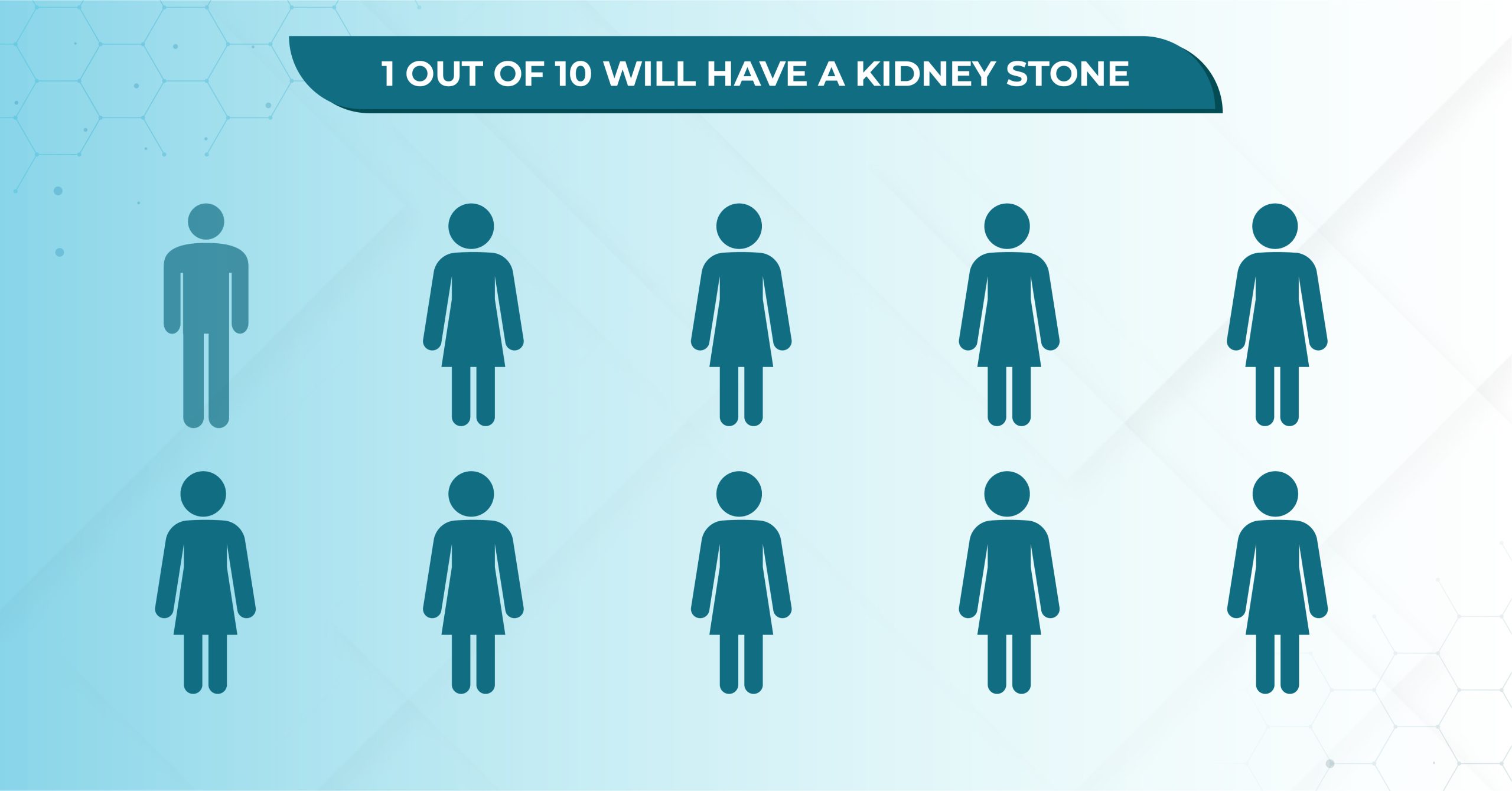
Did you know that more than half a million patients visit emergency departments each year due to kidney stones? It is predicted that one in every ten people may get a kidney stone at some point in their lives. Every year, approximately 12% of Indians are affected by kidney stones, with this percentage rising to as high as 15% in certain regions of India.
Many treatment options for kidney stones are prohibitively expensive, placing them out of reach for a large portion of the population. These costs can be a significant barrier to receiving essential care, leading to untreated or improperly managed conditions. This is why you need to opt for the best as well as cost-effective treatment for kidney stones.
Before we discuss kidney stone treatment alternatives, let us first understand what kidney stones are and how they occur.
Urine stones, sometimes referred to as kidney stones or renal calculi, are solid crystal formations in the urine tract that can cause significant pain and suffering. Stones like this differ in shape, size, and content, and knowing how they develop is critical for prevention and treatment.
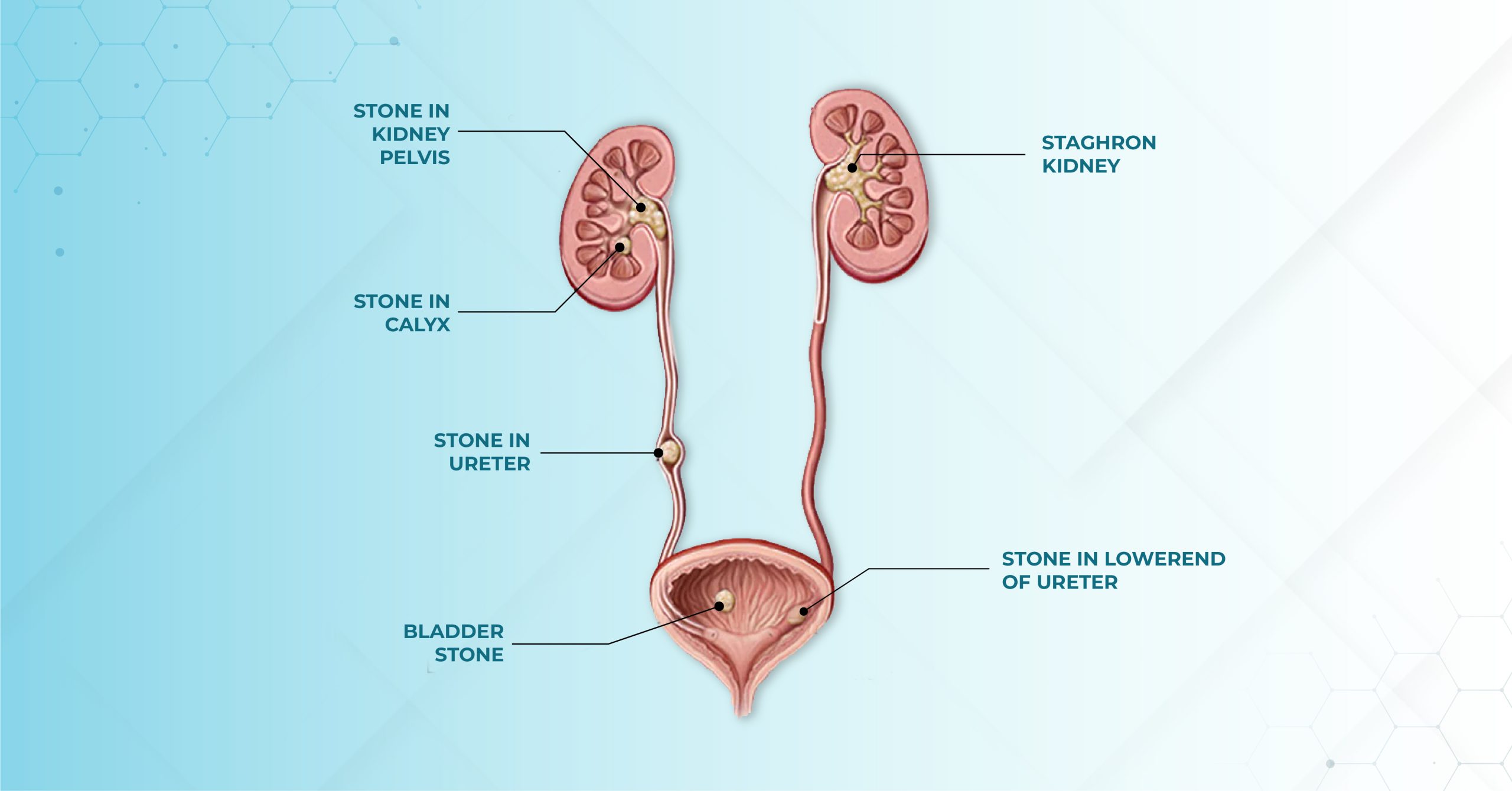
Formation of renal stones:
Renal stones occur when certain chemicals in the urine get very concentrated and solidify.
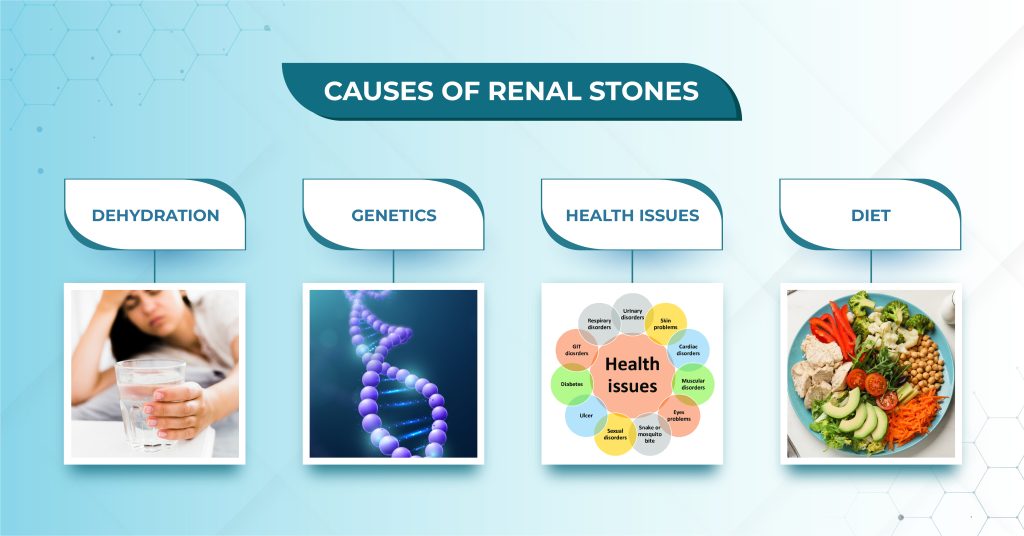
The primary factors contributing to stone formation include:
1. Dehydration: Fewer intakes of fluids can lead to urine concentration, making it easier for minerals to crystallize and form stones.
2. Dietary Factors :A diet rich in protein, salt, and oxalate could raise the probability of stone creation. Oxalate is found in spinach, almonds, and chocolate and can react with calcium to form kidney stones.
3. Medical Issues: Medical conditions such as hyperparathyroidism, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can increase the risk of kidney stone formation.
4. Genetics: Family history of urinary stones can increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing stones.
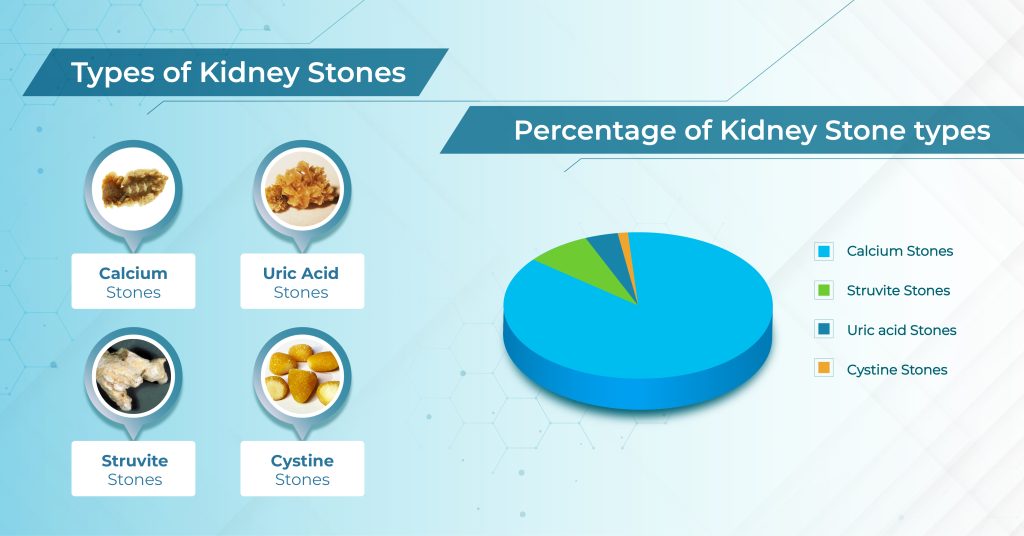
Types of Kidney Stones:
1. Calcium Stones: These are frequent stones in the kidney composed mostly of calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate. High calcium levels in the urine, generally resulting from nutritional or metabolic difficulties, contribute to their creation.
2. Struvite Stones: These stones comprise primarily of magnesium, ammonium, and phosphate. They may develop as a result of certain kinds of infections caused by bacteria in the urinary system.
3. Uric Acid Stones: When urine is too acidic, uric acid crystallizes and forms stones. They can occur as a result of things like a high-protein diet or illnesses like gout that raise the body’s uric acid levels.
4. Cystine Stones: These uncommon stones develop in people with cystinuria, an inherited condition that triggers the kidneys to secrete excessive quantities of cystine, a type of amino acid.
Signs of kidney stones include:
Depending on the size and location of the stone, different urinary stones might cause different symptoms. Typical signs and symptoms include:
- Excruciating pain in the groin, abdomen, side, or back
- Urine containing blood
- Urinating a lot
- Urinating in pain
- Swelling and uneasiness
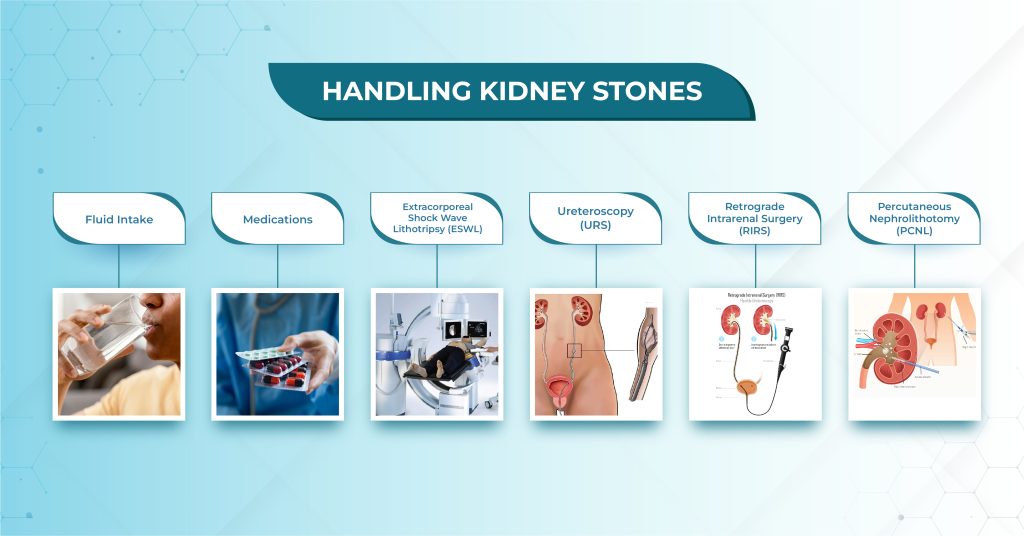
Handling Kidney Stones:
1. Fluid Intake: To flush out the stones and stop them from forming, it is imperative to increase fluid intake. Water is the greatest option since it keeps minerals from crystallizing and helps dilute pee.
2. Medication: Medications are given to help dissolve stones or stop them from forming, depending on the kind of stone. Thiazide diuretics, for instance, can help lower the risk of calcium stone development and the amounts of calcium in the urine.
3. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): The non-invasive Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) technique breaks up the stones into tiny pieces so they can more easily flow through the urinary system.
4. Ureteroscopy (URS) – Ureteroscopy, also known by the name ureterorenoscopy, is a minimally invasive procedure using a ureteroscope to extract kidney stones without incision. Under general anaesthesia, the ureteroscope is passed via the urethra and the bladder to the ureter, breaking the stone with an ultrasonic/electrohydraulic probe. A catheter (double-J stent) is inserted to drain the stone fragments. While the procedure lasts about 60–120 minutes, the pain may take up to 48 hours to relieve from the kidney and abdomen.
5.Retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) – is the least intrusive method of eliminating renal stones within the kidney, utilizing a fibre optic endoscope. In RIRS, the scope is inserted into the kidney’s urine-collecting system via the urethra (the urinary entrance) through the bladder, and the ureter. The RIRS procedure is performed under general anaesthesia for stones less than 20mm in size.
6. Surgery: Surgery may be required to remove the stones in some circumstances. Usually, bigger stones or stones producing significant symptoms are the exception to this rule.
Prevention of Kidney Stones:
Preventing kidney stones requires adjusting life and dietary modifications to reduce the likelihood of stone creation. Prevention measures include:
– Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated
– Limiting the intake of foods high in oxalate, such as spinach and nuts
– Getting enough calcium from food or supplements
– Limiting sodium intake to prevent the excretion of calcium in the urine
– Avoiding excessive consumption of animal protein
At best, kidney stones can be annoying, but at worst, they can be excruciatingly painful. Consult a healthcare practitioner as soon as possible to prevent the condition from growing worse. At Urosonic Day Care, we stand at the forefront of offering non-invasive procedures that prioritize patient comfort and well-being. Visit us at Urosonic Day Care, the best treatment centre for kidney stones in Bangalore, where we aim to alleviate the burden of kidney stones, ensuring a swift and smooth recovery for all our patients. Book your appointment today.